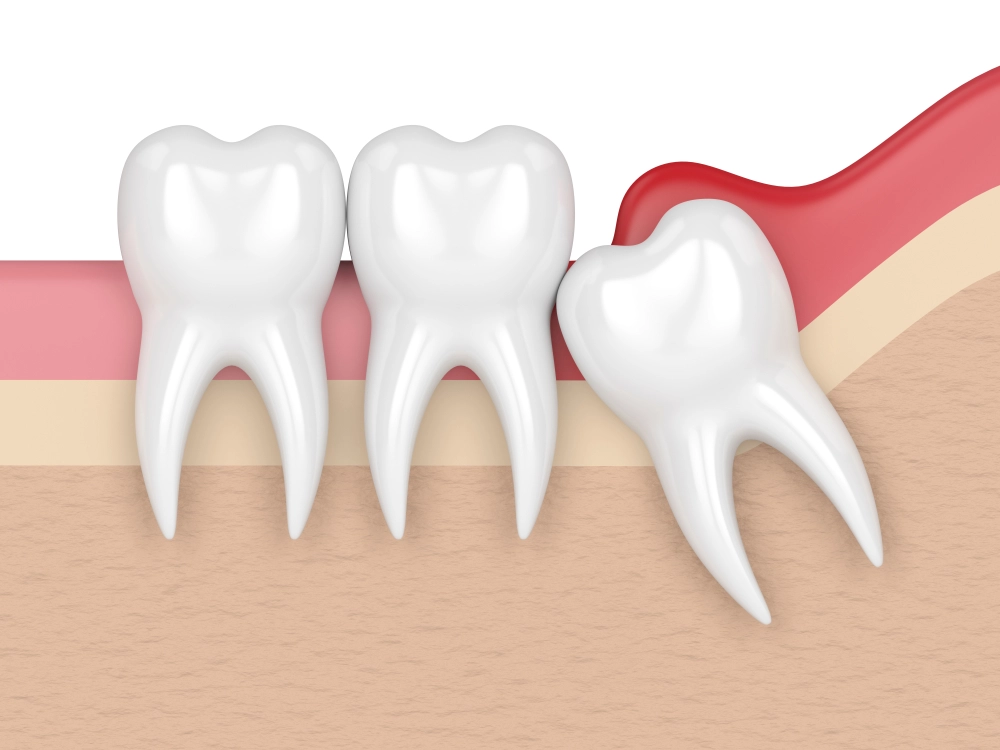
Pericoronitis is a common dental condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the gum tissue surrounding a partially erupted tooth. It often occurs in the lower wisdom teeth, where the tooth does not fully emerge through the gum, leaving a flap of gum tissue that can trap food particles and bacteria. This article aims to explain what pericoronitis is, its causes, symptoms, and the available treatment options.
Understanding Pericoronitis:
Pericoronitis is an oral health condition that occurs when the gum tissue around a partially erupted tooth becomes inflamed and infected. The most common cause of pericoronitis is the presence of a partially erupted wisdom tooth, particularly in the lower jaw. In some cases, other teeth can also be affected.
Causes Of Pericoronitis:
Pericoronitis is primarily caused by the accumulation of food particles and bacteria beneath the gum flap that covers a partially erupted tooth. This trapped debris creates an environment where bacteria can thrive, leading to inflammation and infection. Other factors that may contribute to the development of pericoronitis include poor oral hygiene, inadequate space for the tooth to emerge properly, and trauma to the area.
Symptoms Of Pericoronitis:
The symptoms of pericoronitis can vary in severity but commonly include:
Pain and discomfort in the affected area.
Swelling and redness of the gum tissue around the partially erupted tooth.
Difficulty opening the mouth or chewing.
Foul taste or odor in the mouth.
Discharge of pus or fluid from the gum tissue.
Treatment Options For Pericoronitis:
Conservative Treatment:
In mild cases of pericoronitis, conservative treatment methods may be sufficient. These include:
Warm saltwater rinses to help reduce inflammation and cleanse the area.
Oral hygiene practices, such as gentle brushing and flossing, to remove debris and bacteria.
Over-the-counter pain relievers to alleviate discomfort.
Antibiotics:
Antibiotics for pericoronitis, If the pericoronitis is more severe or has spread to surrounding tissues, the dentist may prescribe antibiotics to combat the infection. It is essential to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve.
Dental Cleaning:
Professional dental cleaning may be recommended to remove plaque, tartar, and debris that are contributing to the infection. This can be done by a dentist or dental hygienist.
Incision and Drainage:
In cases where there is a significant abscess or persistent infection, the dentist may need to make an incision to drain the pus and alleviate pressure. This procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia.
Extraction of the Affected Tooth:
If pericoronitis recurs frequently or becomes chronic, the dentist may recommend extracting the affected tooth. This is usually a last resort when other treatment options have failed or if the tooth is causing ongoing problems.
Prevention Of Pericoronitis:
To reduce the risk of developing pericoronitis, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing. Additionally, visiting a dentist for regular check-ups can help identify any potential issues before they develop into more significant problems. If you have partially erupted wisdom teeth and experience symptoms of pericoronitis, it is essential to seek dental care promptly.
Conclusion:
Pericoronitis is a common dental condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the gum tissue around a partially erupted tooth. It can cause pain, swelling, and difficulty eating or opening the mouth. Treatment options range from conservative measures such as warm saltwater rinses and oral hygiene practices to more invasive procedures like incision and drainage or tooth extraction.